Most people know that tooth decay causes damage to the enamel known as dental cavities. However, did you know that your enamel can become damaged in other ways? One common way enamel becomes damaged is from excess acid that erodes the surface of the teeth. When this acid is caused by bacteria, it is known as tooth decay. However, when the acid is not the result of bacteria, it is simply known as dental erosion.
Although bacteria is by far the most common cause of damaged enamel, dental erosion can occur as a result of:
Diet
There are several different types of foods that can lead to dental erosion. Sugary and starchy foods can cause bacterial growth and additional acid production. Acidic fruits such as apples, citrus, berries, and rhubarb are also another common cause of enamel erosion. Fruit juices also contain excess acid that can result in erosion. Additionally, sodas contain citric and phosphoric acid that can also contribute to erosion.
Digestive Acids
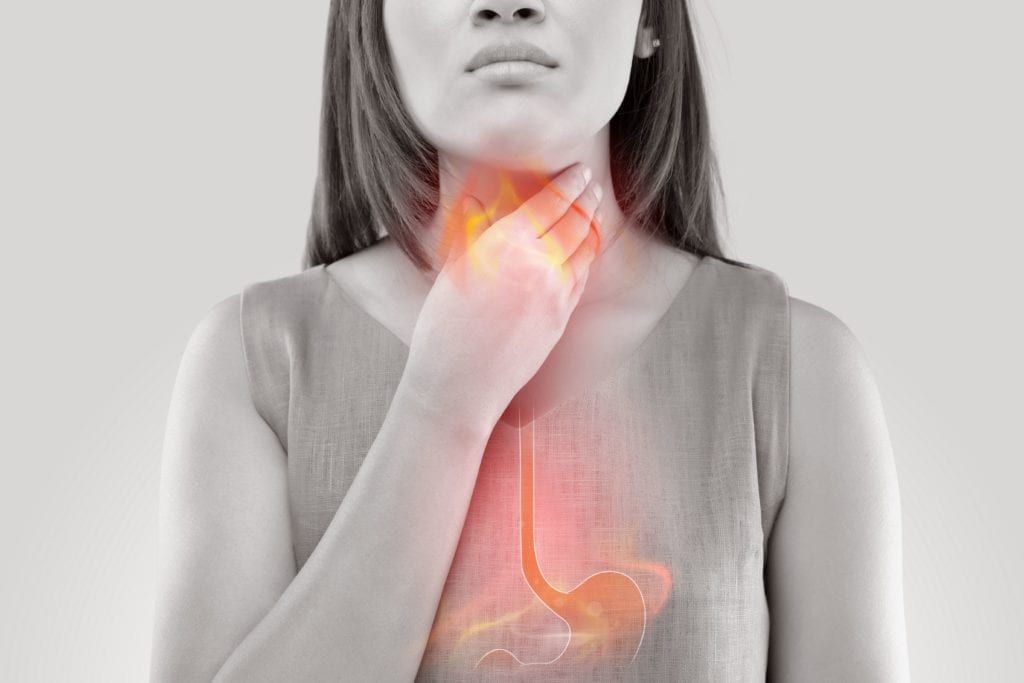
Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) is a common medical condition that causes excess stomach acid to back up into the esophagus. This can increase the acid content in the saliva and cause the teeth to be exposed to higher levels of acid. Additionally, frequent vomiting can also cause acidic erosion of the enamel.
Dry Mouth
Saliva is an essential element in decreasing the amount of acidity in the mouth. However, when not enough saliva is produced, this can cause an increase of acid. Therefore, people with dry mouth are more likely to have enamel erosion. In some cases, dry mouth can be a side effect of certain medications or medical conditions.
Teeth Grinding
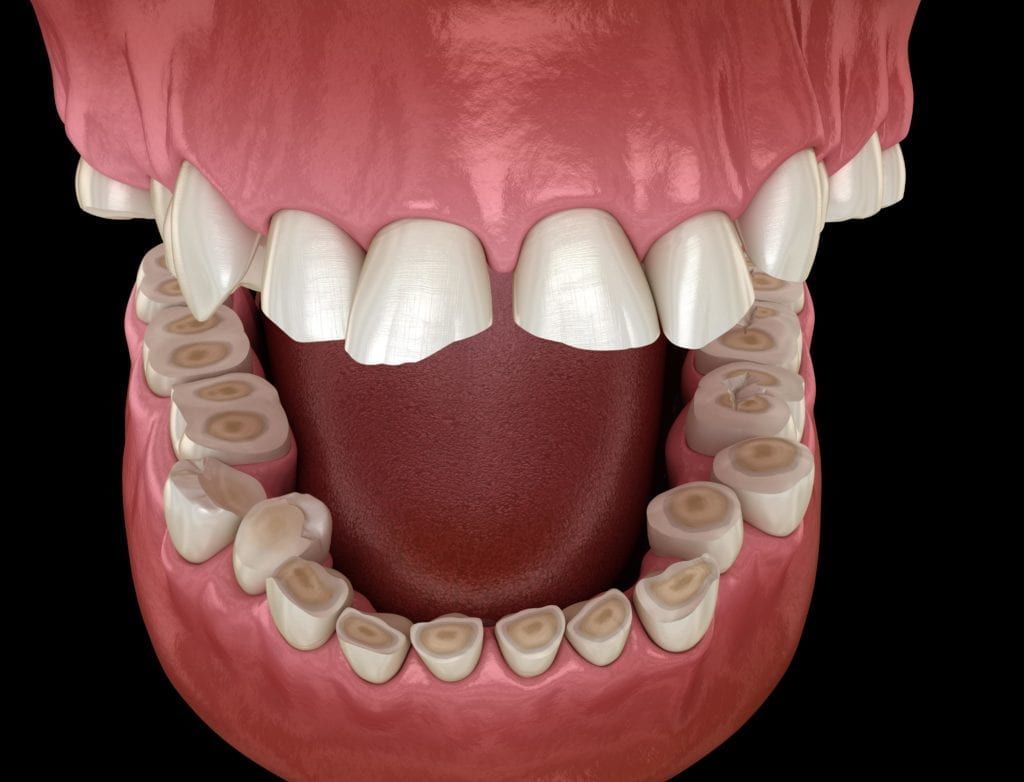
Bruxism, also known as teeth grinding or clenching, damages the teeth by constantly exposing them to stress. Overtime, this causes the enamel to wear down and erode in certain locations.
There are various signs of dental erosion, including:
- Tooth sensitivity
- Discoloration
- Indentations on the surface of the teeth
- Cracks and chips
However, early cases of dental erosion may not be noticeable to anyone but a general dentist. Before the enamel begins to erode entirely, it will need to demineralize. Enamel is composed of 96% minerals, specifically hydroxyapatite. Hydroxyapatite is a combination of calcium and phosphate that are arranged as a crystalline shape. When large amounts of acid comes in contact with the teeth, it breaks the bonds and crystalline structure, inhibiting the tooth’s ability to protect itself.
As you can see, dental erosion poses a similar threat to your teeth as tooth decay. It can be caused from diet, digestive acid, dry mouth, and bruxism, and can cause little to no symptoms depending on how far it has progressed.